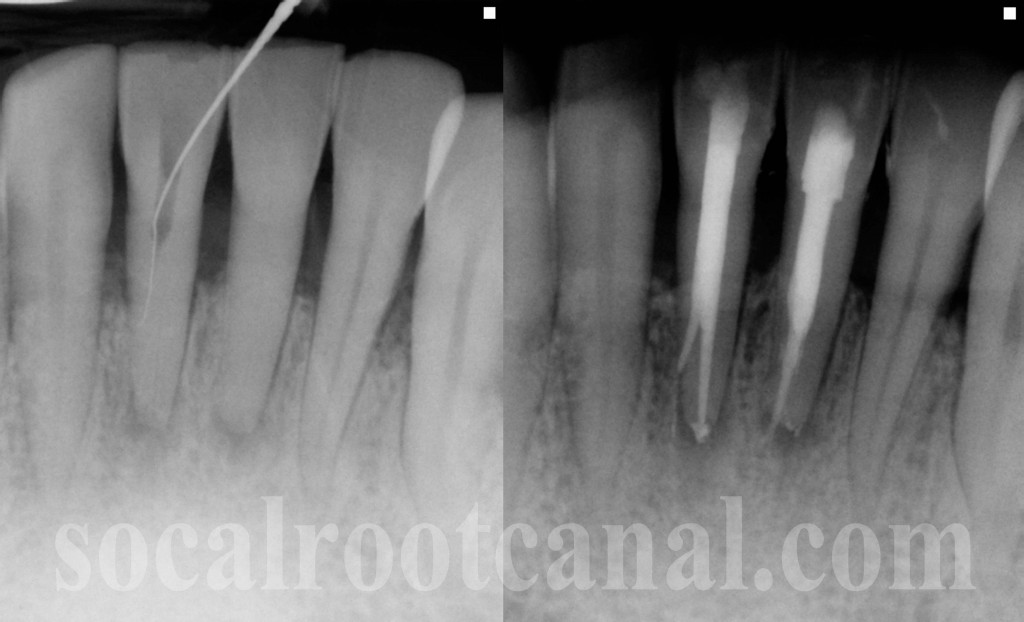
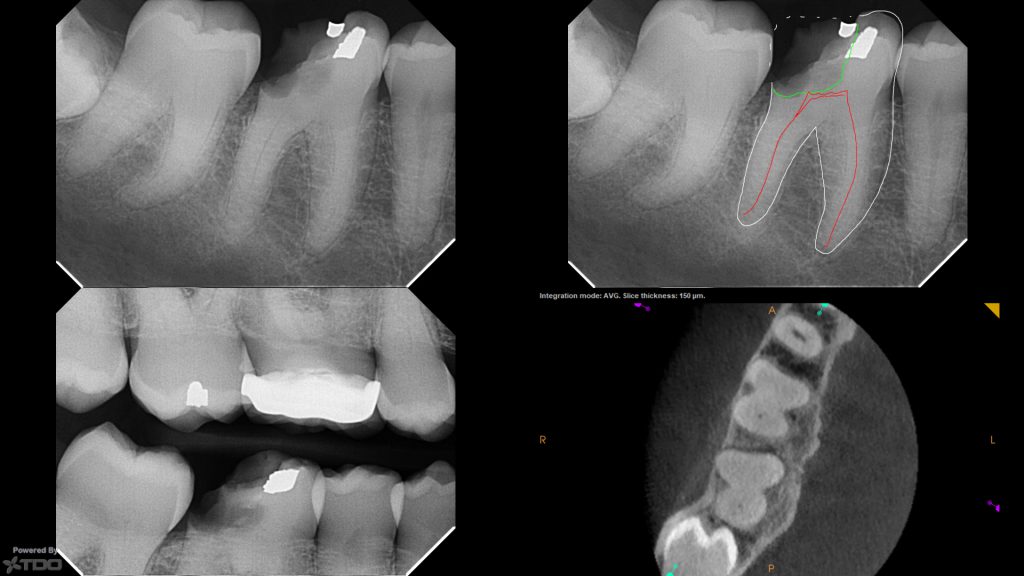
Untreated calcified canal is a complex dental condition that requires specialized attention and treatment. This condition occurs when the root canal becomes calcified due to natural aging processes or trauma, making it challenging for dentists to access and treat the affected area. Understanding this condition is crucial for maintaining oral health and preventing further complications.
Many individuals face dental issues that go unnoticed until they escalate into more severe problems. Untreated calcified canals are one such issue that can lead to severe pain, infection, and even tooth loss if not addressed promptly. This article delves deep into the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for untreated calcified canals, offering valuable insights for both patients and dental professionals.
By exploring the latest advancements in endodontic treatments and expert advice from reputable sources, this guide aims to equip readers with the knowledge necessary to manage and treat untreated calcified canals effectively. Let’s begin by understanding the basics of this condition and its implications on oral health.
Read also:Discovering Evelyn A Comprehensive Guide To Her Life Achievements And Influence
Table of Contents
- What is Untreated Calcified Canal?
- Causes of Calcification
- Symptoms and Diagnosis
- Treatment Options
- Prevention Strategies
- Common Misconceptions
- Importance of Regular Dental Checkups
- Advanced Techniques for Treatment
- Case Studies
- Conclusion and Call to Action
What is Untreated Calcified Canal?
An untreated calcified canal refers to a root canal that has undergone calcification, a natural process where mineral deposits accumulate within the canal, narrowing or completely blocking it. This condition is more common in older adults but can occur at any age due to trauma or inflammation. Calcification makes it difficult for dentists to perform standard root canal treatments, as the canal may no longer be visible or accessible.
The root canal system is crucial for maintaining the health of a tooth, as it houses the pulp, which contains nerves and blood vessels. When calcification occurs, it disrupts this system, potentially leading to infection, abscesses, and tooth loss if left untreated. Understanding the mechanisms behind calcification is essential for developing effective treatment strategies.
Causes of Calcification
Several factors contribute to the calcification of root canals. These include:
- Aging: As people age, the natural mineralization process increases, leading to calcification in various parts of the body, including teeth.
- Trauma: Dental injuries or trauma can stimulate the body’s natural response to heal by depositing minerals, which can lead to calcification.
- Inflammation: Chronic inflammation in the pulp can trigger calcification as a protective mechanism.
- Genetic Factors: Some individuals may have a predisposition to calcification due to genetic factors.
By addressing these underlying causes, dental professionals can better manage and prevent untreated calcified canals.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Identifying untreated calcified canals can be challenging due to their asymptomatic nature in the early stages. However, as the condition progresses, patients may experience:
- Severe tooth pain
- Swelling around the affected tooth
- Sensitivity to hot or cold temperatures
- Discoloration of the tooth
Diagnosis typically involves a combination of clinical examination, radiographic imaging, and advanced diagnostic tools such as cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT). These methods help dentists visualize the calcified canal and plan appropriate treatment.
Read also:Julius De Boer The Inspiring Journey Of A Visionary Leader
Treatment Options
Treating untreated calcified canals requires specialized techniques and expertise. Below are the primary treatment options available:
Root Canal Treatment
Traditional root canal treatment involves accessing the pulp chamber and removing the infected tissue. In cases of untreated calcified canals, dentists may use:
- Microsurgical techniques
- Ultrasonic instruments to locate and remove calcified tissue
- Chemical agents to dissolve calcified deposits
These methods increase the chances of successfully treating the affected tooth while preserving its structure.
Surgical Options
In cases where non-surgical treatments are ineffective, surgical interventions such as apicoectomy may be necessary. This procedure involves removing the tip of the root and sealing the canal to prevent further infection. Surgical options are typically reserved for complex cases where traditional methods fail.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing untreated calcified canals involves maintaining good oral hygiene and undergoing regular dental checkups. Some preventive measures include:
- Brushing twice daily with fluoride toothpaste
- Flossing regularly to remove plaque and food particles
- Using mouthwash to reduce bacterial growth
- Visiting the dentist every six months for professional cleaning and examination
By adopting these practices, individuals can reduce their risk of developing untreated calcified canals and other dental issues.
Common Misconceptions
There are several misconceptions surrounding untreated calcified canals. Some people believe that:
- Calcification is irreversible and cannot be treated
- Root canal treatments are painful and should be avoided
- Only older adults are at risk of developing calcified canals
These misconceptions can hinder timely treatment and lead to unnecessary complications. Educating patients about the realities of untreated calcified canals is crucial for improving outcomes.
Importance of Regular Dental Checkups
Regular dental checkups play a vital role in detecting untreated calcified canals early, allowing for prompt intervention. Dentists use advanced diagnostic tools to identify potential issues before they escalate into more severe problems. By scheduling routine visits, individuals can maintain optimal oral health and address any concerns promptly.
Advanced Techniques for Treatment
Recent advancements in endodontic technology have significantly improved the treatment of untreated calcified canals. Techniques such as:
- Operating microscopes for enhanced visualization
- Laser-assisted treatments to dissolve calcified deposits
- CBCT imaging for precise diagnosis and planning
These innovations have increased the success rates of treating untreated calcified canals, offering patients more effective and less invasive options.
Case Studies
Case studies provide valuable insights into the treatment of untreated calcified canals. For example:
- A 45-year-old patient with a calcified mandibular molar was successfully treated using ultrasonic instruments and chemical agents, preserving the tooth’s structure.
- An elderly patient underwent apicoectomy after traditional root canal treatment failed, resulting in complete resolution of symptoms.
These cases highlight the importance of tailored treatment plans based on individual patient needs.
Conclusion and Call to Action
Untreated calcified canals pose significant challenges in dental care, but with the right knowledge and treatment approaches, they can be effectively managed. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and available treatment options, individuals can take proactive steps to maintain their oral health. Regular dental checkups and adherence to preventive strategies are key to avoiding complications.
We encourage readers to share their experiences or questions in the comments section below. For further information, explore our other articles on dental health and treatment options. Together, let’s prioritize oral health and ensure timely treatment for all dental concerns.
References:
- American Association of Endodontists. (2023). Endodontic Treatment Options for Calcified Canals.
- Journal of Endodontics. (2022). Advanced Techniques in Treating Calcified Root Canals.
- World Health Organization. (2021). Oral Health Guidelines and Recommendations.